Bleeding gums are a classic sign of periodontal disease or gum disease. Sore and painful gums may also be present in patients who have gingivitis, an early stage of gum disease. Gum disease is a progressive disease commonly caused by poor oral hygiene and a lack of dental care in children and adults. Dr. Robert Gauthier and his team at Apex Dental offer periodontal treatments to treat gum disease, no matter the stage or severity. Call Apex Dental today to receive high-quality treatment for sore and bleeding gums and other dental concerns in Northborough, MA.
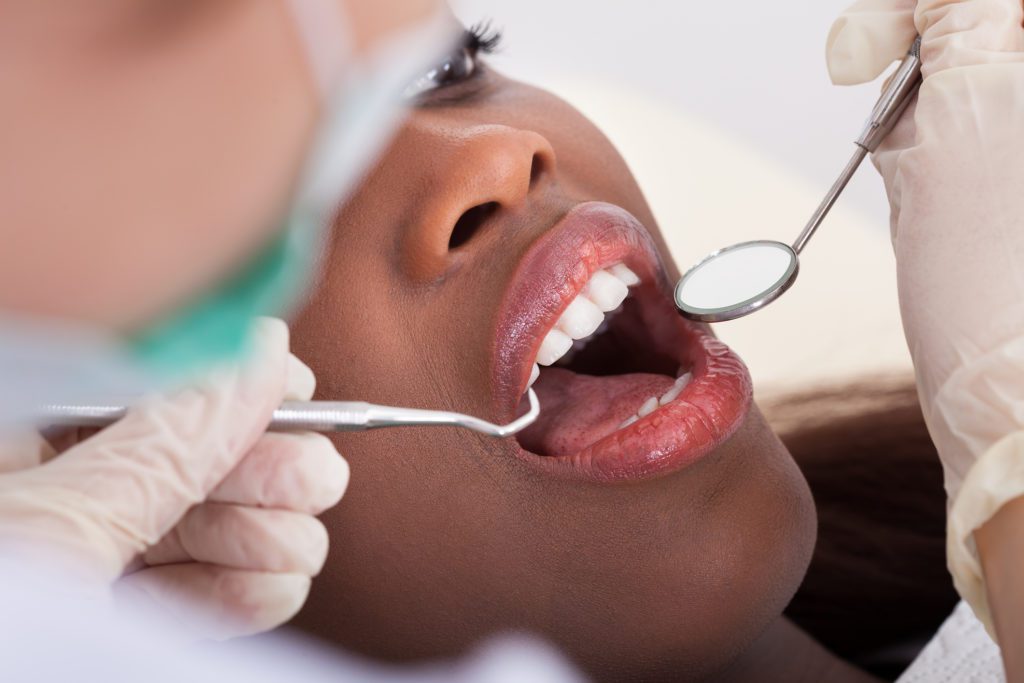
Why Do My Gums Bleed?
Your gums shouldn’t bleed when you brush or floss your teeth. There are a number of reasons why gums bleed. In some cases, it may be a result of aggressive flossing or tooth brushing.
Other times, using a toothbrush with bristles that are too firm can be to blame. While it is important to brush and floss daily, you should be careful to not cut the sensitive gum tissue.
If gums bleed on a routine basis, it may be an indication of the presence of gum disease-causing bacteria. Bacteria can cause the gums to become inflamed and sensitive. Over time the gums begin to pull away from the teeth and can cause bleeding.
It’s common for some people to have bleeding gums during pregnancy. This happens because of hormonal changes in the body. These changes can make your gums more sensitive and more likely to get irritated or swollen, especially when you brush or floss. This condition is called pregnancy gingivitis.
Pregnant women should continue to brush and floss, but be extra cautious around sensitive gum tissue to prevent bleeding. Maintain routine visits to the dentist during pregnancy to monitor gum health.
Bleeding Gums Treatment in Northborough, MA
A dentist should always handle treatment for bleeding gums. Never attempt to self-treat bleeding gums or use over-the-counter medications without the advice of a dental professional. Depending on your condition, there are a number of treatment options for bleeding gums.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis, an early stage of gum disease, is an inflammation of the gums. It is common for people with gingivitis to experience bleeding gums when brushing their teeth or flossing. For gingivitis treatment, the plaque is removed from exposed parts of the teeth and gums. Antibacterial rinses and other aids may be recommended to reduce inflammation and cure gingivitis.
Periodontitis
If you have periodontitis, an advanced form of gum disease, the dentist may need to provide more intensive treatment. Scaling and root planing are procedures that clean the deep pockets of the gums. Dr. Gauthier will use special tools to scrape away plaque and tartar build-up. He’ll remove bacteria from the deep gum pockets where it forms.
Removing the bacteria from the pockets in the early stages of development can help prevent gum recession and tooth loss. In extreme cases, laser dentistry or oral surgery may be necessary.
Bleeding Gums FAQs
Read the answers to these frequently asked questions about bleeding gums in Northborough, MA:
When should I be concerned about bleeding gums?
Every once in a while, brushing too hard or your hand slipping during flossing can cause your gums to bleed. However, it’s important to notice how often they’re bleeding. Call our office if it’s becoming a regular thing and you notice it is happening often. Regular bleeding gums indicate that you’re developing gum disease, which worsens over time.
Should I keep brushing my teeth if my gums are bleeding?
Yes. Though bleeding can make you panic, avoiding brushing your teeth worsens the problem. Gum disease is caused by plaque and bacteria buildup at the gumline. You want to continue to brush your teeth to prevent buildup and remove plaque already on your teeth.
Does gum disease go away?
Gum disease is only reversible if it’s caught and treated promptly. It will not go away without proper treatment and diligent oral healthcare. Gingivitis is the earliest stage and the only one that’s reversible.
Many adults have it and don’t realize it because the symptoms aren’t painful. This is why getting to the dentist is important if your gums are bleeding. Once the bacteria become more aggressive, they start destroying the bone structure.
Do gums grow back?
No, once gum tissue is gone, it’ll rarely grow back. The best way to prevent receding gums is to prevent them from happening in the first place with diligent oral healthcare and preventative measures. If your gum disease advances, you may need gum grafts to cover areas where the gums have receded too far.
Can I treat bleeding gums at home?
While you must tell your dentist about regular gum bleeding, a few things at home can help your situation. Rinse your mouth with warm salt water daily to stop the bleeding and wash bacteria away from the area. A cold compress can help alleviate these symptoms if your gums are tender or painful.
Can dehydration cause bleeding gums?
Yes, hydration is essential for your oral health. Dehydration weakens the gums and makes them more likely to bleed upon contact. Drinking enough water is also important for saliva production. Saliva washes away bacteria and food particles that make you more susceptible to gum disease. Dehydration causes dry mouth and irritates your gums.
Can stress cause my gums to bleed?
Yes, stress can cause your gums to bleed. When you’re stressed, your immune system can weaken, making it harder for your body to fight infections like gum disease. This can lead to inflammation in your gums, which may cause them to bleed when you brush or floss. Stress can also make people clench or grind their teeth, which can irritate the gums.
Can bleeding gums go away on their own?
Bleeding gums might stop on their own if the problem is something simple, like not brushing or flossing well. If you start brushing and flossing better, the bleeding can go away in a few days to a week. But if your gums continue to bleed or the problem gets worse, it could be a sign of gum disease.
Take care of your gums early to prevent more serious problems. Regular dental cleanings and checkups also help keep your gums healthy.
Request a Dental Consultation Today
Routine dental health exams can help prevent the spread and progression of gum disease. Our Apex Dental dentists visually screen for gum disease at every scheduled checkup. Catching gum disease in the earliest stages often means you can get more conservative treatment.
We serve Northborough, Shrewsbury, Westborough, and surrounding communities with compassionate and personalized dentistry. Call Apex Dental today at (508) 506-1691. You can also request an appointment online today.
